AppsSensorsComputersLightingComponentsSecurityEnergyEntertainmentAppliancesHouseholdTelecomHubsNetworkingSelf-HostedCloudPhonesRadiosPlugsBulbsSwitchesLaptopsMini PCSoCCPUGPUNPUMemoryMotherboardNVMEWiFiFansLocksDoorbellsCamerasAlarmsSensorsMetersPlugsSolarBreakersTVsStreamingSpeakersAudio SystemsSmart KitchenSmart RefrigeratorsSmart DishwashersSmart Coffee MakersSmart OvensWashersDryersWater HeatersRefrigeratorsVacuumsMopsToothbrushesMirrorsScalesHumidifiersButtonsClimatePresenceZigbee HubZ-Wave HubWiFi HubBluetooth HubMatter & Thread HubLoRa HubMulti-Protocol HubSwitchEnclosureCurtainsWiFi APRoutersTablets
How to Choose the Right Smart Home Platform and App
Published: June 1st 2025 @ 5:15PM
Navigating the Pros and Cons of Open Source, Self-Hosted, and Cloud-Based Solutions
Creating a seamless and reliable smart home environment starts with selecting the right platform app. Whether you're tech-savvy or a beginner in smart home automation, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of open source, self-hosted, and cloud-based solutions is essential. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of each option, highlighting key considerations to help you choose the ideal platform while ensuring your smart home remains future-proof, versatile, and user-friendly.
Open Source Platforms: Flexibility and Transparency
Open-source platforms, such as Home Assistant, are favored by enthusiasts for their transparency, community-driven development, and endless customization options. They offer complete visibility into the platform's inner workings, allowing users to modify and tailor the software to their specific needs. However, this flexibility often requires greater technical know-how and involvement in community forums or documentation for troubleshooting and advanced customizations.
Self-Hosted Platforms: Reliable Local Control
One of the significant advantages of self-hosted platforms is that they function independently of internet connectivity. Solutions like Home Assistant and Hubitat provide robust local control, ensuring your smart home devices remain operational even during internet outages. Self-hosting offers privacy advantages, as your data remains local, reducing security risks and avoiding dependence on cloud-based services which may experience downtime or service interruptions.
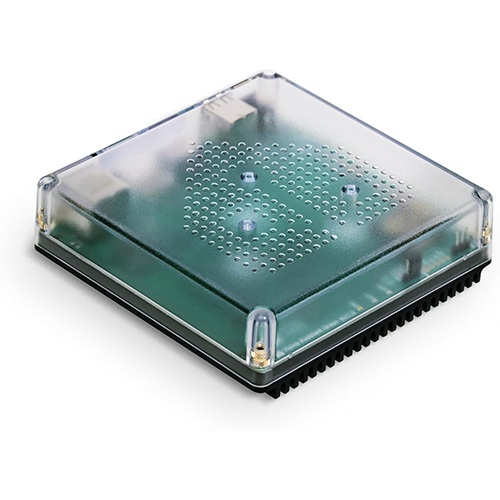
Featured Product
Home Assistant Green | Smart Home hub
Where to Buy
Supported Connectivity
wifi
bluetooth
mqtt
http
matter
zigbee
localAdditionally, local-only platforms provide superior response times and reduced latency, which is especially beneficial for critical security or lighting automations. However, they require ongoing maintenance, hardware investments, and a basic understanding of networking and system administration, presenting a moderate learning curve for beginners.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Convenience and Accessibility
Cloud-based smart home platforms, such as Apple Home, Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Samsung SmartThings, offer unparalleled convenience and ease of use. These solutions feature straightforward setup processes, intuitive interfaces, and seamless integrations with popular devices. Their reliance on cloud services allows users to access and control their smart homes remotely, receiving real-time updates and notifications from anywhere.
Despite these benefits, cloud reliance introduces potential privacy concerns, subscription costs, and dependency on continuous internet connectivity. A cloud outage or internet downtime can temporarily disable your smart home functionality, causing inconvenience, particularly in critical applications such as home security.
Avoiding Platform Lock-In
While many users prefer the polished interfaces provided by popular cloud solutions, it is important to avoid locking yourself into a single ecosystem. To maintain flexibility, consider using smart home hubs or gateway devices that support multiple communication protocols, such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, and especially Matter/Thread. This cross-protocol support helps future-proof your setup by allowing easy integration of new devices and technologies without overhauling your existing setup.
The Rise of Matter/Thread: The Future of Smart Home Connectivity
Matter, supported by Thread, represents the next evolution of smart home connectivity. Matter ensures interoperability across brands and devices, simplifying integrations and reducing compatibility headaches. For instance, platforms like Home Assistant integrate seamlessly with Matter devices, providing users with effortless setups and broader device compatibility.
Cloud-driven platforms, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Home, also embrace Matter, highlighting its importance in creating a universal smart home standard. Thread's robust, mesh-networking capability offers reliable, low-power connectivity, crucial for battery-operated devices and sensors scattered throughout your home.
Wi-Fi: A Key Component of Your Smart Home
WiFi remains indispensable due to its high bandwidth, widespread adoption, and robust reliability, especially suitable for high-data usage devices such as cameras, streaming hubs, and voice assistants. Integrating devices via WiFi ensures rapid communication, higher-quality streams, and enhanced responsiveness. Nevertheless, balancing Wi-Fi usage with lower-bandwidth protocols like Zigbee or Thread can help maintain network performance.
Future-Proofing Your Smart Home
Ensuring your smart home remains relevant requires forward-thinking planning. Prioritize purchasing devices compatible with emerging protocols such as Matter/Thread. Invest in smart hubs or gateways supporting multiple standards to easily integrate future devices. Regularly updating firmware and software also ensures compatibility with newer standards and enhances security.
Viewing and Accessing Your Smart Home
Smart home platforms offer various ways to interact with and view your devices. Hub devices with integrated screens, such as the Amazon Echo Show 5 and Google Nest Hub Max, provide a visual interface, enabling convenient interactions like monitoring security camera feeds, controlling smart lighting, or viewing weather forecasts at a glance. Voice assistants and mobile apps supplement these physical hubs, providing versatile options for interaction based on your location and preferences.
Automations: The Backbone of Smart Home Efficiency
Automations significantly enhance the functionality and convenience of your smart home by executing predefined actions based on specific triggers, such as time, sensor activation, or device status. Self-hosted platforms excel at managing complex, reliable automations locally, ensuring immediate execution even without internet connectivity. For example, automations can trigger lights to turn on at sunset, lock doors automatically when leaving home, or adjust thermostats based on occupancy sensors.
Cloud-based solutions also support automations, but dependency on the cloud introduces latency, potential downtime, and reliance on external service availability. While suitable for non-critical applications, these constraints highlight why local automations are superior for reliability and responsiveness.

Practical Use Cases of Automations
- Security: Automations can lock doors, activate cameras, and send alerts if suspicious activity is detected.
- Energy Efficiency: Automatically adjust thermostats based on occupancy or outside weather conditions to reduce energy consumption.
- Convenience: Trigger lighting scenes or multimedia setups when entering specific rooms or at scheduled times.
- Safety: Integrate smoke or water leak detectors to shut off appliances or send immediate alerts in emergency scenarios.
By understanding the detailed pros and cons of open source, self-hosted, and cloud-based smart home platforms, as well as leveraging future-proof protocols like Matter/Thread, you can confidently select a smart home platform app that meets your current needs and adapts seamlessly to future advancements.
Further Reading:
Further Reading:

